Problem statement
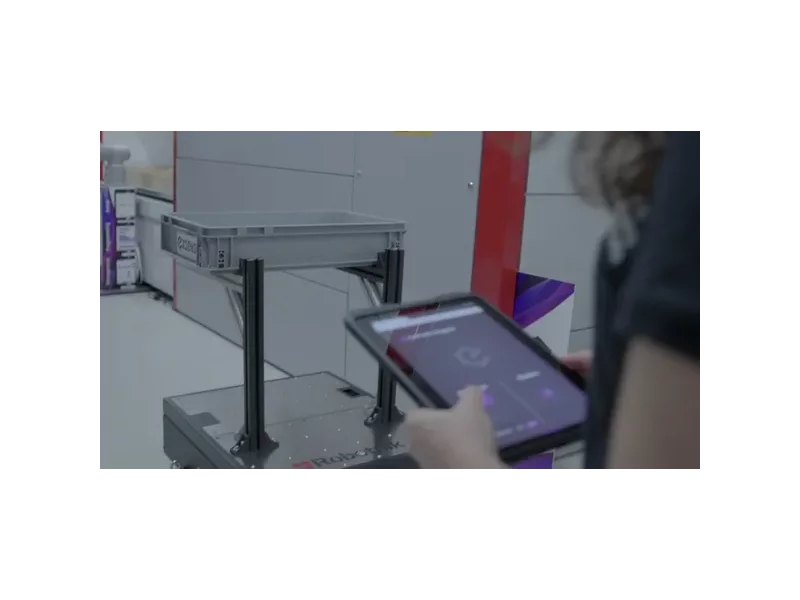
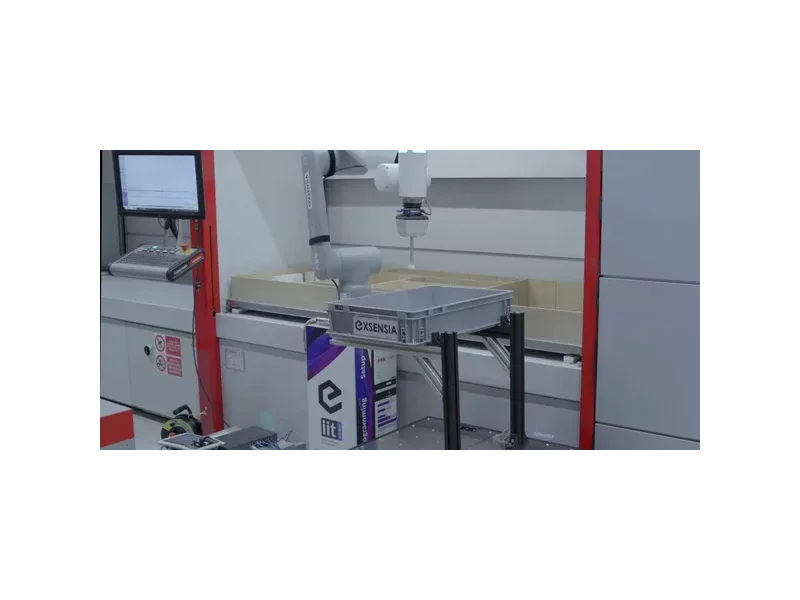
The solution tackles the challenge of programming and coordinating a mobile base and an industrial robot to automate the loading and unloading of a vertical storage system. Traditional methods require expert knowledge and complex coding, especially when synchronizing mobile platforms with manipulators working at variable heights and positions. We address this by enabling intuitive, visual programming of both the mobile base and the robot arm, significantly reducing engineering effort and improving flexibility in deploying such automation in dynamic environments.
Main outcome
The solution introduces an advanced software platform that enables intuitive programming and coordination of both a mobile robotic base and a stationary robot for automated interaction with a vertical storage system. Technological innovation lies in the ability to program complex, synchronized tasks involving mobile manipulation through an intuitive, no-code interface. Users can define behaviors and workflows visually, without writing a single line of code, making robotic automation accessible to operators without technical backgrounds.